Scepter Scientific Inc. Integrated Vision Technologies
728x90 ad placeholder
Address
- 7820 Cypress Creek Ct.
- Pleasanton, CA 94588
- USA
General Information
- info@scepter.net
- Sales: sales@scepter.net
- Webmaster: webmaster@scepter.net
Scepter Scientific. in a joint Venture with Crane & Co., developed a variety of products and sensors to authenticate currency based upon security features within the note. This patented technology has led to a variety of patented sensors found in currency handling equipment throughout the world
Scepter Scientific is now a leader in security thread detectors and we continue to develop new currency fitness and authentication technologies to meet customers growing requirements.
Several of the sensor technologies are outlined in the following descriptions:
Currency Inspection
| Electro-optical currency soil sensor | |
| Denomination insensitive soil level measurement | |
| Industry standard measurement of currency fitness |
A soil sensor was developed to automatically determine the fitness of currency as it is processed on a high speed currency sorter system. The soil sensor is an Electro-optical device which illuminates currency at specific points along the note and measures the reflected light to determine the brightness level. A structured illumination system and collimated detector provide measurements of exceptional accuracy that are virtually independent of the note positioning under the inspection station.
A complex measurement algorithm was tailored to provide an exact duplicate of the established manual measurement technique resulting with a measurement index that is equivalent to the previously established standards.
This sensor was designed to meet stringent absolute accuracy, stability, and repeatability requirements while constrained to mechanical and electrical requirements of the previously existing currency sorter system. This development program concluded with a soil sensor significantly exceeding all performance requirements and is now successfully operating at over 150 installations across the United States.
Hand Held Metallized Thread Detector
| Verifies metallized threads embedded in documents | |
| Low power battery technology | |
| Microprocessor adjustable sensitivity |
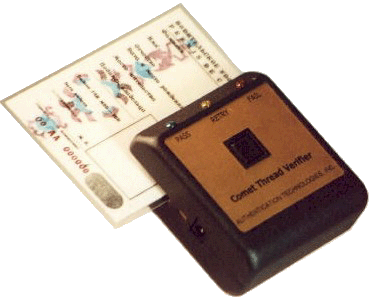
A complimentary handheld instrument and thread pattern was developed to provide a low cost document verification method. As in other embedded thread applications, the embedded thread allows for a visual verification, as well as a more secure electrical detection of the thread..
The thread and the unit were optimised to prevent invalid readings that may be caused by any conductive materials that may be added to documents as in the case of forgeries.
The unit’s verification method involves a scanning capacitive sensor array, which is used to detect a specific metallized pattern. The sensor array was designed to allow for a wide range of thread positioning within the document caused by variations in the manufacturing process of the embedding of the thread in the document.
The unit’s mechanics were modeled after a handheld credit card reader to give the user an intuitive, easy to use interface. A three LED display informed the user of the result of the scan.
High-Speed Metallized Thread Reader
| Reads Denomination of Currency | |
| High-Speed DSP Processing |
An instrument was developed to denominate currency embedded with a COMET® thread pattern in high-speed transport applications. The COMET® thread, developed by Scepter Scientific Inc., consists of discrete sections of fully metallized threads binary encoded in such a manner as to produce unique codes that are impervious to note position and orientation across a sensor. Also, the reader/thread combination must be able to withstand one broken section of thread per note, as might occur in the normal wear and tear of a bank note.
The reader scans the note with a capacitive detector array, and, using a proprietary deskewing algorithm, determines the best fit denomination. In order to meet the high-speed requirements of the application, a Digital Signal Processor (DSP) had to be used. The DSP also had to perform signal conditioning to increase the signal-to-noise ratio, which was degraded by artifacts such as the transport belts rubbing the front of the sensor and the inconsistent pressure of the note against the front of the sensor.
The DSP indicates the denomination via an LCD display, which is linked to the DSP via a serial link. A second serial link is used to configure the sensor. This second port along with discrete outputs are used to inform the host system of the denomination and quality of the signal.
Wide Edge Lead Currency Thread Detection System
A document verification device detects the presence of a metal security thread embedded in a document such as currency paper. The device includes a sensor pad arrangement and corresponding signal processing electronics. The arrangement includes a single central sensing pad flanked by an array of twenty-seven pairs of outer pads. Each pair of outer pads in the array is electrically connected together. Every pad is made of conductive material. The width dimension of each outer pad in the array is greater than the width of the security thread. Each outer pad in the array is preferably angled to improve the reliability of detection of the security thread. The electronics generates a square wave oscillator signal that is applied to the outer array pads in a pattern that includes two adjacent pairs of array pads having the positive voltage level portion of the square wave signal applied thereto, and the following two adjacent pairs of array pads having the negative voltage level portion of the square wave signal applied thereto. This pattern is sequenced in time over the entire array. The document to be verified is transported with respect to the sensor pad arrangement such that the wide edge of the document is the leading edge. As the thread passes over the array, the pattern is sequenced throughout the pads fast enough such that, at a point in time, the thread will bridge the central sensing pad with a pair of outer two pads first having the positive voltage level portion of the square wave signal applied thereto, and then later the thread will bridge the central sensing pad with the same pair of outer two pads now having the negative voltage level portion of the square wave signal applied thereto. Since the thread is metallic, it will capacitively couple the square wave signal into the central sensing pad. The electronics senses the signal coupled to the sensing pad and interprets a valid security thread as being present in the currency from certain characteristics of the sensed signal.
Microwave Security Thread Detector

A security thread detector for verifying the authenticity of banknotes. In the preferred embodiment, the invention comprises a housing with a passage through which banknotes can be passed, wherein the housing also comprises a wave guide, a microwave oscillator for generating microwaves and two resonating slots on a wall of the wave guide, and a microwave detector. After a banknote is inserted through the passageway, the microwave diode produces an analog signal that is proportional to the microwave strength. The diode and the slots are arranged such that the radiated power from each slot is one hundred eighty degrees out-of-phase. If a banknote has no security thread, then the detector receives a balanced signal. If the banknote contains a security thread, the thread interferes with one of the radiating slots. This interference causes an imbalance condition and a corresponding signal is sent from the detector diode. The resulting signal is then sent to a microprocessor which activates an appropriate indicator. This indicator notifies the user of the presence or absence of a security thread; thus, the user can determine whether the banknote is counterfeit.